Path of preparation (Must watch above video)
All Topics
Board preparation
Board Revision
Extra for mains
Mains Revision
Extra for NEET
NEET Revision
Extra for Advanced
Advanced Revision
😊....End of the Chapter….😊
Ray Optics
INTRO
In this
chapter we learn about different natural phenomena which is due to the ray
nature of light like Reflection, Refraction etc. As we know that we are able to
see each things due to light and one of the nature of light is its ray nature which
we see in this chapter.
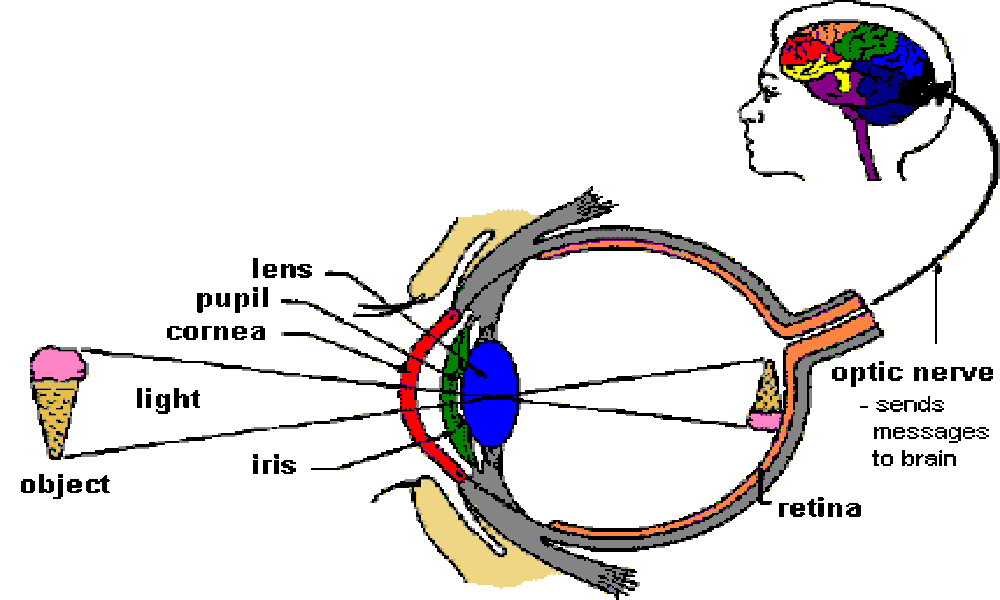
LIGHT
Light is a form of energy which
enables a person to see an objects.
RAY AND BEAM OF LIGHT
The direction or path along
which, light energy travels in a medium is called a ray of light.
It is represented by a straight line on which arrow is marked.
Object is any matter which has
identifiable boundary. In optics the ray of light is emerging from the objects
as a convention to form there image.
TYPE OF OBJECTS
a) Luminous object
b) Non- Luminous object
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
LAWS OF REFLECTION
1. The
incident ray, reflected ray and the normal at the point of incident all three
lie in the same plane.
2. The
incident angle and reflected angle are always equal.
TYPES OF REFLECTION
1. Regular
reflection
2. Irregular
reflection
IMAGE
TYPES OF IMAGE
2. Virtual
image
MIRROR
TYPES OF MIRROR
1) Plane
mirror
There are two
type of spherical mirrors are there
a) Concave spherical mirror
b) Convex spherical mirror
3) Parabolic
mirrors
REFLECTION THROUGH PLANE MIRROR
IMAGE FORMATION BY PLANE MIRROR
1) Image is always virtual.
2) Image is always erect.
3) Image is always form behind
the mirror.
4) The size of image is always
equal to the size of object.
5) The distance of image from
mirror is always equal to the distance of object from mirror. That is the
distance of object and image both are equal from the mirror.
1) Centre
of curvature
2) Radius
of curvature
3) Pole
4) Principle
axis
5) Focus
The point at
which paraxial rays ( that is rays parallel to principle axis and also close to
principle axis ) seems to emerging after reflection through mirror is called
focus ( this definition is for convex mirror)
OR
6) Focal
length
7) Aperture
8) Focal
plane
REFLECTION THROUGH SPHERICAL
MIRROR
IMAGE FORMATION BY SPHERICAL
MIRROR
RULES OF IMAGE FORMATION BY
SPHERICAL MIRRORS
IMAGE FORMATION BY CONCAVE MIRROR
a) When
object is at infinite ( at very large distance ).
Nature of image
b) When
object is beyond the Centre of curvature .
Nature of image
c) When
object is present at Centre.
Nature of image
d) When
object is in between focus and Centre.
Nature of image
e) When
object is present at focus.
Nature of image
f) When
object is in between focus and pole.
Nature of image
IMAGE FORMATION BY CONVEX MIRROR
Nature of image
RELATION BETWEEN FOCAL LENGTH AND
RADIUS OF CURVATURE
R = 2 f
As shown in figure
Angle AFB is an exterior angle
( CB = CP ) Approx
( For small Ɵ tanƟ = Ɵ ) ………………………………(i)
In tringle AFB
( For
small Ɵ tan2Ɵ = 2Ɵ ) ……………………….(ii)
From
(i) and (ii)
CP = 2 FP
R = 2 f ( CP = R
and FP = f )
MIRROR FORMULA
MAGNIFICATION
Object is any matter which has identifiable boundary. In optics the ray of light is emerging from the objects as a convention to form there image.
CP = 2 FP
R = 2 f ( CP = R and FP = f )





















No comments:
Post a Comment